With the upgrading of domestic production capacity, cross-border e-commerce has experienced rapid development in recent years. In 2023 alone, China's cross-border e-commerce imports and exports reached 2.38 trillion yuan, marking a year-on-year increase of 15.6%.
In the initial stages of entering the cross-border e-commerce market, small and medium-sized enterprises often face logistical challenges, such as uncertainty about how to ship products and how to choose logistics platforms. This article aims to provide solutions for cross-border e-commerce logistics, helping businesses that have recently ventured overseas or are planning to do so to overcome these logistical difficulties.
Cross-Border E-commerce Logistics
Cross-border e-commerce logistics refers to a series of logistics processes and services involved when Chinese enterprises engage in e-commerce activities with other countries. These services encompass various stages, including product procurement, warehouse management, order processing, packaging, transportation, customs clearance, and more, ensuring that goods are ultimately delivered safely and accurately to consumers worldwide.
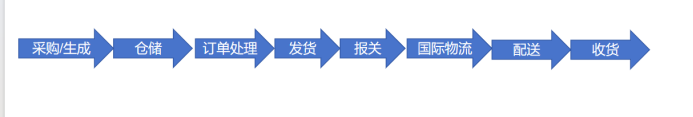
The Complete Process of Cross-Border E-Commerce Logistics.
The entire process of cross-border e-commerce logistics mainly includes the following key steps:
-
Procurement or Product Production: Overseas enterprises first purchase goods from suppliers. For those with their own factories, they produce best-selling products based on selection processes and transport the goods to the warehouse.
-
Warehousing: After arriving at the warehouse, the warehouse staff need to process the products, including sorting, shelving, packaging, and labeling, ensuring the goods comply with the regulations and standards of both the exporting and importing countries.
-
Order Processing: After consumers place orders on the platform, the e-commerce enterprise processes the orders, selecting different packaging and logistics methods based on product categories, profit margins, target countries, logistics costs, and delivery timelines.
-
Shipping: After the order processing stage, the goods are transported to customs via the chosen logistics method.
-
Customs Declaration: Upon arrival at customs, the goods undergo customs declaration, which includes preparing customs documents, submitting declaration applications, paying tariffs, undergoing customs inspections, and obtaining clearance certificates to ensure the goods legally enter the destination country.
-
International Logistics: After clearing customs, the goods enter the international logistics transportation phase. This phase is the most time-consuming part of the entire process. Depending on the transportation method, logistics company, and destination country, the duration can vary, typically ranging from 3 to 30 days.
-
Destination Country Customs Clearance: After the goods arrive in the target country, the local customs conduct clearance procedures, including submitting import declarations, paying import duties and value-added taxes, and passing product inspections and quarantines.
-
Domestic Delivery in the Target Country: Local courier or logistics companies handle the final delivery of the goods, marking the end of the logistics process.
-
Confirmation of Receipt: Once the buyer receives the goods, they confirm receipt.
The main models of cross-border e-commerce logistics include:
The logistics models for cross-border e-commerce generally include Direct Mail, FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon), Overseas Warehousing, and Dedicated Logistics. Below are their definitions and advantages/disadvantages:
| Logistics Model | Definition | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Direct Mail | After a user places an order, the seller directly ships the product to the buyer through a logistics company. |
● Simple process: Only requires packaging and labeling; the logistics company handles the rest. ● Global coverage: Logistics companies can be freely chosen, with worldwide reach. ● No overseas storage costs: Products are shipped directly from the seller’s country, eliminating overseas storage expenses. |
● Long delivery times: Involves international logistics, which can be time-consuming and complex. ● High logistics costs: Non-bulk shipments result in higher costs. ● Lack of scalability: Orders are processed individually, making it cumbersome for large order volumes. |
| FBA Logistics (Fulfillment by Amazon) | Sellers store their products in Amazon warehouses, and Amazon handles the entire logistics process, including storage, packaging, shipping, and returns. |
● Sellers can focus on sales: Amazon handles all logistics, allowing sellers to concentrate on selling. ● Improved customer satisfaction: FBA is known for its high-quality service and efficient logistics. ● Increased sales: Participation in Amazon Prime can boost sales. |
● High costs: Amazon’s fees are generally higher compared to other logistics providers. ● Complex inventory management: Sellers need to spend more effort managing inventory stored in Amazon’s warehouses. ● High after-sales costs: Sellers cannot immediately inspect returned products, and buyers must pay return fees and handling costs when returning items to Amazon warehouses. |
| Overseas Warehousing | Sellers establish warehouses in the target market’s country or region and store products in advance. After a user places an order, the product is picked, packaged, and shipped directly from the overseas warehouse. |
● Short delivery times: Local warehouses significantly reduce delivery times. ● Lower logistics costs: Local shipments reduce logistics expenses. ● Reduced taxes: Overseas warehousing can help lower tariffs and value-added taxes. |
● High storage costs: Building and maintaining warehouses require significant investment, including hiring local staff. ● High inventory costs: Products are transported from the seller’s country to the overseas warehouse, incurring costs that may not be recoverable if inventory is not sold. ● Currency exchange risks: Sellers face financial risks due to currency fluctuations. |
| Dedicated Logistics | Sellers collaborate with logistics companies that provide end-to-end logistics services, including pickup, packaging, shipping, and customs clearance. |
● Sellers can focus on sales: Third-party logistics companies handle the entire logistics process, allowing sellers to focus on e-commerce operations. ● Resource integration and professional service: Logistics companies are more experienced and professional in handling logistics. ● Improved customer satisfaction: Professional logistics services enhance user satisfaction. |
● High costs: Comprehensive logistics services often come with higher fees. ● Limited coverage: Some logistics companies may only serve specific countries, limiting their reach. ● Data leakage risks: User data is shared with third-party logistics companies, posing potential data security risks. |
In both domestic and international markets, there are numerous companies providing cross-border e-commerce logistics services. Based on market share, this article lists 10 logistics companies most commonly used by cross-border e-commerce companies:
-
SF Express (顺丰速运) Founded in 1993 and headquartered in Shenzhen, China, SF Express is a globally renowned comprehensive logistics service provider known for its high-quality services and fast delivery. It holds a leading market share domestically and has expanded its international business to over 200 countries and regions.
-
China Post Express & Logistics (中邮速递易购物流) A subsidiary of China Post Group, China Post Express & Logistics specializes in overseas shopping and forwarding services. With a long history and headquartered in Beijing, it offers postal, courier, logistics, and e-commerce services, boasting a vast domestic and international network and stable market share.
-
4PX Express (递四方) Established in 2004 and headquartered in Shenzhen, 4PX Express focuses on cross-border e-commerce logistics, providing one-stop solutions including global warehousing, delivery, and returns. It has become a leader in this field with operations worldwide.
-
YTO Express (圆通速递) Founded in 2000 and headquartered in Shanghai, YTO Express is one of the largest private courier companies in China. It has rapidly expanded its international business while maintaining a strong domestic presence, securing a significant market share.
-
Yunda Express (韵达速递) Established in 1999 and headquartered in Shanghai, Yunda Express leverages its extensive domestic network to expand internationally, offering efficient logistics solutions and holding a notable market share in the domestic courier industry.
-
Cainiao Network (菜鸟网络) Founded in 2013 by Alibaba Group and headquartered in Hangzhou, Cainiao Network builds a smart logistics network driven by big data and technology. It integrates domestic and international logistics resources, increasingly influencing the global logistics industry.
-
Deppon Logistics (德邦物流) Established in 1996 and headquartered in Shanghai, Deppon Logistics is a leader in China’s less-than-truckload (LTL) logistics sector. It has recently expanded into international logistics, providing standardized and refined logistics solutions with a growing market share in niche markets.
-
DHL-Sinotrans (中外运敦豪) Founded in 1986 as a joint venture between Deutsche Post DHL and Sinotrans, and headquartered in Beijing, DHL-Sinotrans offers global express, air freight, ocean freight, and supply chain management services, holding a leading position in the international courier market.
-
JD Logistics (京东物流) Originating in 2007 and independently operated with its headquarters in Beijing, JD Logistics is the self-operated logistics arm of JD Group. With a focus on unmanned technology and intelligent supply chains, it has expanded its business across China and globally, steadily increasing its market influence.
-
ANE Logistics (安能物流) Established in 2010 and headquartered in Shanghai, ANE Logistics started as a LTL express company and has grown into a comprehensive logistics enterprise offering courier, express, and full-truckload services. It holds a high market share in the LTL sector and is gradually expanding its international logistics services.
These companies play a significant role in the cross-border e-commerce logistics industry, providing diverse and efficient solutions to meet the growing demands of global trade.
The cost and expenses of cross-border e-commerce logistics
The costs and expenses of cross-border e-commerce logistics are relatively complex to calculate due to the lengthy process and the various fees incurred at each stage. These primarily include logistics transportation fees, customs duties, warehousing costs, and more.
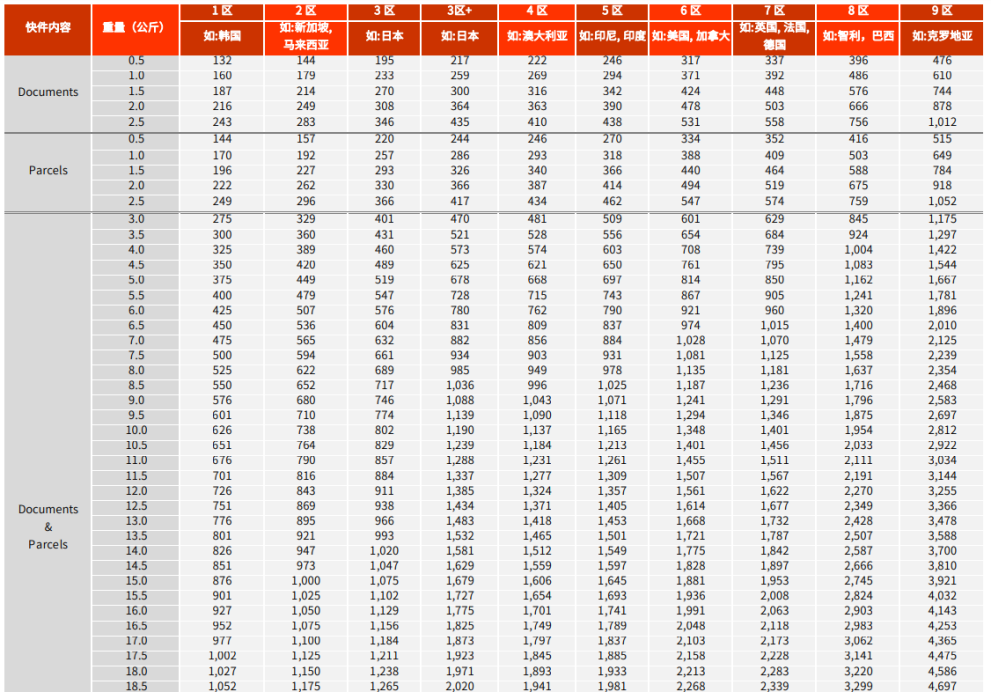
Logistics transportation costs
Logistics transportation costs vary depending on the logistics model chosen by the seller, the logistics company, the volume and weight of the goods, and the destination country. Taking SF Express's direct mail service as an example, if we mail a document weighing less than 0.5 kilograms to South Korea, the cost is 132 RMB; if mailed to Singapore, the cost is 144 RMB. Below is the detailed pricing information:
Customs duties
The calculation of customs duties can be divided into three steps:
-
Determine the Tariff Classification Number (HS Code) Different goods correspond to different tariff rates. By confirming the HS Code, you can identify the applicable tariff rate for the goods in the target country. You can log in to the customs website of the target country, enter the HS Code, and check the tariff rate.
-
Calculate the Duty Base The duty base is usually the CIF value of the goods, which includes the Cost, Insurance, and Freight.
-
Apply the Tariff Rate Apply the tariff rate to the duty base to calculate the payable customs duty. For example, if the CIF value of the goods is 1,000andthetariffrateis101,000andthetariffrateis101,000 * 10% = $100.
Warehousing costs
Warehousing costs are typically calculated based on the quantity, volume, and storage duration of the goods. You can choose a suitable warehousing method, such as self-owned warehouses, third-party warehouses, or cloud warehouses. The costs mainly include: warehouse rent or construction expenses, labor costs for warehouse management personnel, order processing fees, loading and unloading fees, utilities, and more.
Packaging costs
Packaging costs involve ensuring that products are properly packaged to comply with the regulations of the target country and to prevent damage during transportation. The specific packaging costs vary depending on the type of product.
Cross-Border E-Commerce Logistics Distribution by Country
Global Package Volume Rankings
According to the "2023 China Cross-Border E-Commerce Logistics Industry Blue Book" published by Xiaosheng Research Institute, the top 10 countries receiving the most packages from China in 2022 were: the United States, Japan, the United Kingdom, Germany, Canada, France, Russia, Australia, Brazil, and Spain.
China-US Logistics Routes
Despite fluctuations in China-US trade due to US protectionism, the US remains a primary target for Chinese enterprises expanding overseas. Several Chinese cities, including Shenzhen, Beijing, and Guangzhou, have established point-to-point logistics routes to the US. These routes typically utilize air or sea freight, with air freight taking 3-10 days and sea freight taking 15-30 days. Major service providers in China include China Post, SF Express, YTO Express, ZTO Express, and Yunda Express. Upon arrival in the US, local logistics companies such as USPS and FedEx handle the final delivery.
China-Japan Logistics Routes
Cross-border e-commerce trade between China and Japan continues to grow, reflecting strong market demand and potential. By 2025, the China-Japan cross-border e-commerce market is expected to reach $28 billion. Coastal cities like Shanghai, Ningbo, and Qingdao offer direct logistics services to Japan. Air freight typically takes 2-5 working days, while sea freight takes 7-15 working days. Service providers in China include EMS, SF Express, YTO Express, ZTO Express, and Yunda Express. In Japan, local logistics companies such as Japan Post, Yamato Transport, and FedEx Japan complete the last-mile delivery.
China-Russia Logistics Routes
Driven by the Belt and Road Initiative and significant international changes in 2024, China-Russia trade relations have strengthened, fostering rapid growth in cross-border e-commerce. Cities in northeastern China, such as Harbin and Suifenhe, have established dedicated logistics routes to Russia. Land transport takes 7-20 days, while air freight takes 3-7 working days. Chinese logistics companies like China Post, SF Express, YTO Express, ZTO Express, and Yunda Express provide cross-border logistics solutions, while Russian Post, DPD Russia, SDEK, and CDEK handle the final delivery. With both governments promoting trade facilitation, the China-Russia cross-border e-commerce market is poised for further expansion.
FAQs
How to Handle Cross-Border E-Commerce Logistics Shipments
- Choose a Logistics Method: Select air or sea freight based on delivery time requirements, product value, weight, volume, and category.
- Select a Logistics Provider: Partner with reputable domestic and international logistics companies such as DHL, FedEx, UPS, TNT, EMS, SF Express, China Post Express & Logistics, 4PX Express, YTO Express, and Yunda Express.
- Compliant Packaging and Labeling: Ensure products are packaged according to international standards to prevent damage during transit. Attach clear shipping labels, HS codes, and necessary customs documents.
- Customs Clearance: Follow the customs declaration and clearance procedures mentioned in this article.
Differences Between Cross-Border E-Commerce Logistics and Traditional International Freight
Cross-border e-commerce logistics differs from traditional international freight in terms of target audience, shipping methods, and compliance requirements. Cross-border e-commerce logistics caters to SMEs and individual consumers, focusing on small-batch, high-frequency orders, personalized services, and rapid response. Traditional international freight serves large enterprises, prioritizing cost efficiency and standardized import/export procedures.
How Long Does Cross-Border E-Commerce Logistics Take?
Delivery times depend on the shipping method, logistics provider, and destination country. For example, air freight to the US typically takes 3-7 working days, while express services like DHL, FedEx, and UPS can deliver to major cities within 2 working days. Sea freight generally takes 15-30 days, with expedited options taking 7-15 days.
How to Prevent Loss or Damage of Cross-Border E-Commerce Packages
To minimize the risk of lost, damaged, or customs-seized packages:
- Partner with reputable logistics providers.
- Use standardized packaging to protect goods during transit.
- Comply with customs regulations, avoiding misdeclaration of product value or name.
- For hazardous goods, obtain necessary certifications and register with airlines.
- Purchase insurance and carefully select logistics modes to reduce risks.
- Understand destination country customs requirements and declare product values accurately to avoid clearance issues.