作者:郭增涛
Overview of On-Page SEO
What is On-Page SEO?
On-Page SEO refers to the practice of optimizing individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and attract organic traffic. It involves implementing best practices that directly influence ranking factors as outlined by Google. Common tasks related to On-Page SEO include optimizing for search intent, title tags, internal linking, URLs, and more.
The Difference Between On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO
On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO are two major components of Search Engine Optimization (SEO), working together to improve a website’s ranking on Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). Below are the key differences between the two:
On-Page SEO focuses on optimizing internal elements of a website, including content, HTML elements, and site architecture. It involves direct edits and adjustments to web pages to enhance their visibility and ranking on search engines.
Key Elements of On-Page SEO:
- Keyword Research: Identifying and incorporating relevant keywords into content.
- Visual Content: Optimizing images and videos with alt text and proper formatting.
- Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Crafting concise, keyword-rich titles and descriptions for each page.
- Structured Markup: Using schema markup to help search engines understand page content.
- Page URLs: Creating short, descriptive, and keyword-rich URLs.
- Internal Linking: Building a logical internal linking structure to improve navigation and page authority.
- Mobile Responsiveness: Ensuring the website is optimized for mobile devices.
Goal of On-Page SEO: To ensure website content aligns with user search intent, provides valuable information, and is technically optimized for search engine crawling and indexing.
Off-Page SEO
Off-Page SEO refers to optimization activities conducted outside the website, primarily aimed at increasing its online visibility and reputation.
Key Elements of Off-Page SEO:
- Backlinks: Acquiring high-quality, relevant backlinks from authoritative websites, which is one of the most critical factors in Off-Page SEO.
- Social Media Marketing: Promoting content and engaging with audiences on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
- Brand Mentions: Earning mentions of your brand on other websites, even without a direct link.
- Online PR Activities: Participating in guest blogging, interviews, and other publicity efforts to boost credibility.
Goal of Off-Page SEO: To build the website’s authority and trustworthiness, indirectly improving its ranking on search engines.
Importance of On-Page SEO
On-Page SEO enhances a webpage’s visibility, accessibility, and user experience by optimizing elements like content, keywords, title tags, meta descriptions, image alt text, internal linking, mobile responsiveness, and page speed. This not only helps search engines better understand the page content but also ensures it matches user search intent. By attracting and retaining more visitors, On-Page SEO increases organic traffic and potential leads, making it an essential part of any successful online marketing strategy.
In summary, while On-Page SEO focuses on optimizing internal website elements to improve search engine visibility, Off-Page SEO emphasizes external activities like backlink building and social media engagement to enhance the site’s authority and reputation. Both are crucial for achieving higher rankings and driving organic traffic.
Keyword Research
In On-Page SEO, keyword research and application are central to optimizing website content, keyword placement, and SEO strategies. By deeply understanding user search intent and preferences, businesses can significantly improve their rankings on Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), increase visibility, attract more potential users, and ultimately drive business growth and brand promotion.
1. Determine Target Country and Language
Search habits vary across different countries and languages. When selecting keywords, it’s crucial to consider the search behaviors of your target audience. Accurately matching keywords to your target market can greatly enhance search rankings.
2. Choose Keywords with Appropriate Competition Levels
The keywords you target may vary depending on your website’s stage of development. Tools like KD (Keyword Difficulty) filters can help identify high-search-volume, low-competition "treasure" keywords, which are easier to rank for.
3. Cover Mainstream Search Demand
Search demand for keywords can be multifaceted, but only 10 positions are available on the first page of search results. Ensuring your keyword research covers mainstream search demands can significantly boost website traffic and rankings.
4. Keyword Research Tools
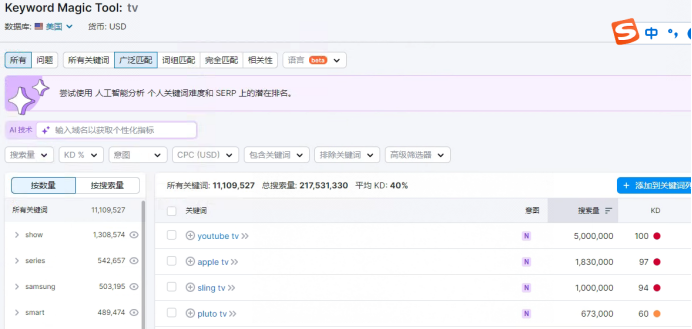
For keyword demand research, tools like SEMrush’s Keyword Magic Tool are highly effective. For example, it can help analyze long-tail keyword search volumes and difficulty levels for terms like "tv" in the U.S..
Creating High-Quality Content
After conducting keyword research to identify the search terms and long-tail keywords used by your target audience, along with their search volume and competition levels, the next step is to create high-quality content.
Content Creation
Develop high-quality, original content that provides value to users and is relevant to the target keywords. The content should comprehensively address user queries and offer unique perspectives or solutions.
Natural Integration
Incorporate keywords naturally into the content, avoiding over-optimization or keyword stuffing. Keywords should appear in key positions such as:
- Title Tag
- Subheadings (Headers)
- First and last paragraphs of the body text.
Keyword Distribution
Keywords should be evenly distributed throughout the content, avoiding excessive concentration in any single paragraph. The use of keywords should enhance content quality and user experience, rather than solely focusing on SEO.
Avoid Keyword Stuffing
Modern search engines can detect and penalize keyword stuffing. Therefore, keywords should feel natural and contextually relevant, not forced.
By following these guidelines, you can create content that not only ranks well in search engines but also genuinely engages and satisfies your audience.
Optimizing Page Elements
Title Tags
Title Tags are one of the most critical elements in page optimization. They define the theme of a webpage and are displayed as the page title in search results. An effective Title Tag not only attracts user clicks but also clearly communicates the core content of the page to search engines.

Here are some key points to follow when crafting Title Tags:
-
Include Keywords: Ensure the title contains the target keyword(s) to help search engines understand the page’s topic and improve its ranking for that keyword.
-
Conciseness: Keep the title concise and clear, ideally within 50-60 characters, to ensure it displays fully in search results without being truncated.
-
Relevance: The title should accurately reflect the page’s content, aligning with user search intent and the information provided on the page.
-
Attractiveness: Use compelling and creative language to grab users’ attention and increase the click-through rate (CTR).
-
Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Overloading the title with keywords can lead to penalties from search engines.
Meta Descriptions
Meta Descriptions are another critical component of page optimization. While they are not a direct ranking factor for search engines, they play a vital role in attracting user clicks and enhancing the visibility of a page.

Here are some key points to consider when writing meta descriptions:
-
Conciseness and Relevance: Meta descriptions should be concise and to the point, typically within 150-160 characters, to ensure they display fully in search results while accurately reflecting the page's main content.
-
Keyword Inclusion: Include target keywords in the meta description to improve the page’s relevance in search results. When the keywords match the user’s query, search engines may bold them, increasing visual appeal.
-
Click-Worthy Language: Craft meta descriptions that are compelling and encourage users to click. Use strong language and a clear value proposition to spark curiosity and interest.
-
Avoid Misleading Information: Ensure the meta description aligns with the page content to avoid misleading users, which can lead to high bounce rates and negatively impact SEO.
-
Uniqueness: Each page’s meta description should be unique, even for pages with similar topics. This helps differentiate content and improves user engagement.
-
Call-to-Action (CTA): Incorporate clear CTAs like “Download Now” or “Learn More” to encourage user interaction and boost engagement.
By following these guidelines, you can create effective meta descriptions that enhance visibility, attract clicks, and improve SEO performance.
H Tag Optimization
H tags should be arranged in a logical hierarchy, from H1 (most important) to H6 (least important), helping both search engines and users quickly understand the structure of the page content.
Key Points for H Tag Optimization
-
Uniqueness of the H1 Tag: Each page should have only one H1 tag, which typically represents the main title of the page. It serves as a strong content signal to search engines.
-
Keyword Integration: Naturally incorporate target keywords into H tags, especially in H1 and H2 tags. This enhances the page’s relevance and improves search engine rankings.
-
Content Summarization: H tags should summarize the main idea of the content below them, providing a clear information framework for both readers and search engines.
-
Avoid Overuse: Avoid excessive use of H tags, especially in succession or for non-heading content. This can confuse search engines about the page’s structure.
-
Proper Use of H2 and H3 Tags: Use H2 and H3 tags appropriately to segment content, providing additional context for search engines and improving the page’s readability.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively optimize H tags to enhance both SEO performance and user experience.
Image Optimization
Adding images to your content can increase your chances of ranking in Google Image Search, which is a great way to drive more traffic to your website. To optimize images effectively, focus on the following aspects:
1. Compress Images
To improve page loading speed, use tools to compress images and reduce file size without compromising visual quality. This is crucial for both user experience and SEO, as faster-loading pages rank better in search results.
2. Use Descriptive Filenames
Image filenames should be descriptive and relevant to the content, avoiding generic names like "IMG_1234.jpg." Instead, use names that reflect the image’s content, such as "puppy-playing.jpg." This helps search engines understand the image better and improves its chances of ranking in image searches.
3. Importance of Alt Text
The ALT attribute provides a textual description of the image for search engines, which is essential for ranking in image searches. Additionally, ALT text improves accessibility for visually impaired users who rely on screen readers.
4. Writing Alt Text
Alt text should be concise and descriptive, summarizing the main content of the image. Avoid unnecessary details or keyword stuffing, and keep it under 125 characters for clarity.
5. Alt Text and Keywords
Incorporate keywords naturally into the alt text to enhance the image’s relevance to the page content. However, avoid over-optimization, as excessive keyword use can harm SEO.
6. Image Relevance
Ensure that images are closely related to the page’s topic and provide useful visual information. Relevant images enhance content engagement and improve the overall SEO performance of the page.
By implementing these strategies, you can optimize your images for both search engines and users, ultimately driving more traffic to your website and improving its SEO performance.
Website Structure and Navigation
SEO-Friendly URL Structure
Using short, descriptive URLs that highlight the core theme of a page is highly beneficial. Parts of the URL can be displayed as breadcrumbs in search results, allowing users to quickly assess whether the search result is relevant to their needs.
A well-structured URL not only improves user experience but also helps search engines better understand the content and context of the page, ultimately enhancing SEO performance .
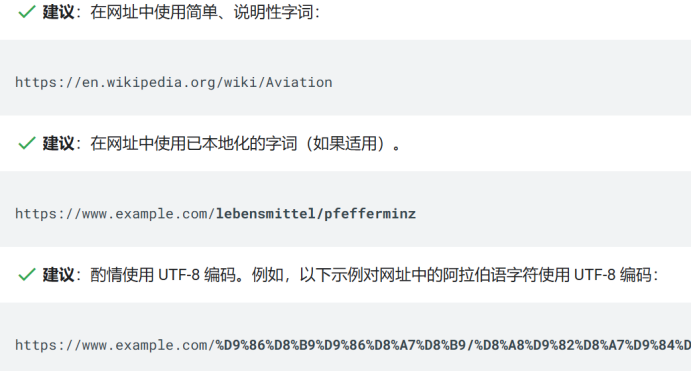
-
Keep it Short and Clear: URLs should be concise and intuitive, avoiding long and complex structures. This makes them easier for users to remember and helps search engines quickly parse them.
-
Include Keywords: Naturally incorporate target keywords into the URL. This enhances the page’s relevance and improves its ranking in search engine results.
-
Maintain a Clear Hierarchy: Use slashes (/) to separate different levels of directories, reflecting the website’s navigation structure and clearly indicating content categories.
-
Avoid Parameters and Symbols: Minimize the use of dynamic parameters and symbols such as question marks (?), equal signs (=), and hash symbols (#). These can make URLs appear cluttered and are less friendly to search engine.
-
Use Hyphens for Separation: If the URL contains multiple words, use hyphens (-) to separate them instead of underscores or other characters. This improves readability.
-
Use Lowercase Letters: Consistently use lowercase letters to avoid duplicate content issues caused by inconsistent capitalization.
-
Avoid File Extensions: Generally, avoid including file extensions like .html or .aspx in URLs unless there is a specific requirement for certain page types.
-
Track and Analyze: Use tools to monitor URL performance, analyze user behavior, and track search engine crawling to make necessary adjustments.
Internal Linking Strategy
Adding internal links at appropriate places within your web content helps visitors navigate your site and increases the likelihood of them finding the information they need. At the same time, internal links assist search engines in discovering all the pages on your website. Anchor text is also a dimension that search engines use to judge the relevance of web pages.
Below is an example from Google Search Central documentation on internal linking. When mentioning related terms or articles, adding internal links allows users to delve deeper into the content.
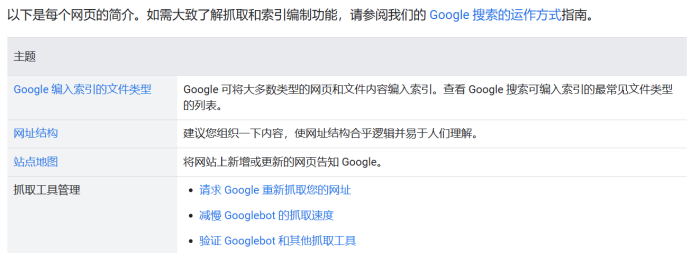
Considerations for Internal Link Building
-
Link Relevance: Ensure internal links point to content that is relevant to the current page’s topic. This helps search engines understand the organization and hierarchy of your website’s content .
-
Anchor Text Selection: Use descriptive anchor text that includes keywords but remains natural and contextually appropriate. Avoid over-optimization, as it can negatively impact SEO .
-
Content Coherence: Integrate internal links naturally within the content to enhance its flow and readability. Links should feel organic, not forced or out of place .
-
Link Depth: Link not only to the homepage and main category pages but also to deeper content pages. This helps search engines discover and index all important pages .
-
Avoid Broken Links: Regularly check and fix broken or dead links to ensure all internal links are active. Broken links can harm user experience and SEO performance .
-
Link Diversity: Use a variety of internal links across multiple pages of your website. Avoid repeating the same link structure on all pages, as it can limit the effectiveness of your internal linking strategy .
By following these guidelines, you can build a robust internal linking strategy that improves both user experience and search engine visibility.
On-Page SEO Advanced Techniques
Optimizing for Featured Snippets
Featured Snippets are a special section on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) that provides direct answers to user queries. They typically appear in the form of paragraphs, lists, or tables.
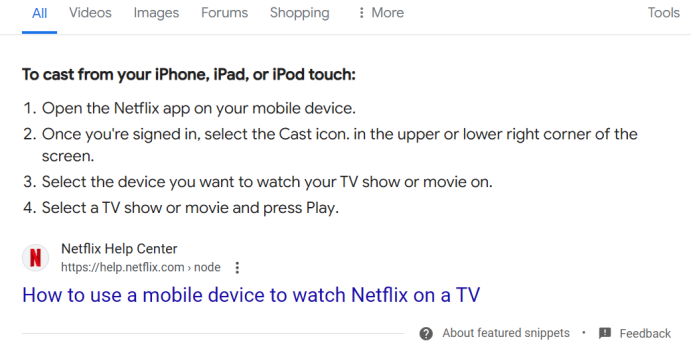
Optimizing for Featured Snippets: Benefits and Considerations
-
Increase Visibility: Featured Snippets appearing at the top of search results can significantly enhance a webpage’s visibility and click-through rate (CTR), often outperforming traditional top-ranked results.
-
Match User Intent: Optimize content to align with user search intent by providing concise and direct answers. This increases the likelihood of securing a Featured Snippet position.
-
Content Formatting: Use clear formats such as lists, steps, or tables to improve content readability and help search engines easily identify the answer.
-
Keyword Optimization: Ensure target keywords are placed in critical areas like the title, body text, and meta description to enhance relevance to the query.
-
Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Use keywords naturally to avoid over-optimization, which can make content appear unnatural or lead to penalties from search engines.
-
High-Quality Content: Provide accurate, high-quality content to establish authority and reliability, which helps build trust with search engines.
-
Mobile Optimization: With the increasing use of mobile devices for searches, ensure your webpage performs exceptionally well on mobile platforms.
-
User Experience: The ultimate goal is to deliver an exceptional user experience. Featured Snippets should attract users to explore your website further, increasing engagement and time spent on the site.
Structured Data
Structured data (also known as Schema Markup) is code added to your webpage to help search engines better understand your content. It enables richer information to be displayed in search results, such as ratings, prices, and images, which can boost CTR and improve user experience.
By implementing these strategies, you can optimize your content for Featured Snippets and structured data, enhancing both search engine performance and user engagement.
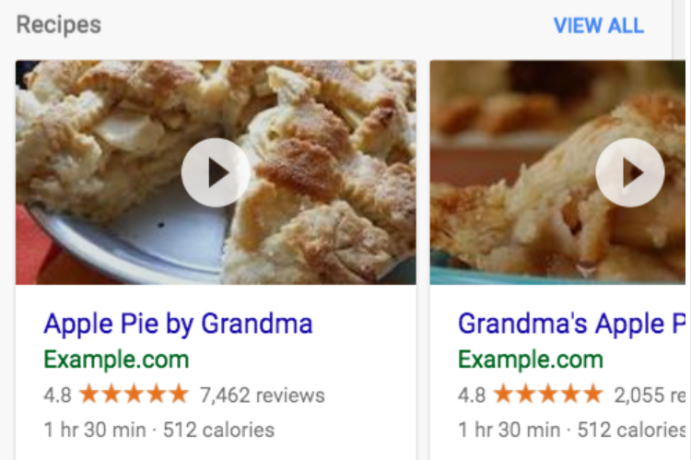
-
Accuracy: Ensure Schema tags accurately describe the page content and data type, avoiding errors or misleading information.
-
Follow Schema.org Guidelines: Schema Markup is based on Schema.org specifications. Adhere strictly to these guidelines to ensure search engines can correctly interpret the data.
-
Test and Validate: Use tools like Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to test and validate Schema code, ensuring there are no errors or omissions.
-
Regular Updates and Maintenance: As Schema.org specifications evolve and website content changes, regularly review and update Schema tags to maintain their relevance and accuracy.
-
Mobile Optimization: With the rise of mobile searches, ensure Schema tags are effective on mobile devices, providing a consistent user experience.
-
Diverse Content Types: Schema tags can be applied to various content types, including products, articles, events, and people. Choose the appropriate Schema type based on the page content.
-
Avoid Duplication: Avoid using multiple Schema tags for the same content on a single page, as this can confuse search engines.
-
Performance Considerations: When adding Schema tags, consider page performance to ensure the additional code does not negatively impact loading speed.
-
Monitor Effectiveness: Use analytics tools to track the impact of Schema tags on SEO and user behavior, and make adjustments as needed to optimize results.
By following these best practices, you can effectively implement Schema Markup to enhance search engine understanding, improve user experience, and boost your website’s visibility and click-through rates.
Website Speed Optimization
Page load speed, also known as page speed, is a metric that measures the time it takes for a user to open a webpage until the page is fully rendered. Fast page loading provides a better user experience, reduces waiting time, and increases the likelihood of users engaging with other content on the website. This is crucial for overall user interaction and satisfaction.
Core Web Vitals (CWV) play a vital role in Google optimization, directly impacting a website’s ranking performance on Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) and user experience.

Core Web Vitals Components
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures the time it takes for the main content of a page to load and render completely. Ideally, this should be completed within 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID): Reflects the delay between a user’s first interaction (e.g., a click) and the browser’s response. It should be kept under 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Evaluates unexpected shifts in the position of elements during page loading. The goal is to maintain a CLS value below 0.1.
Methods to Improve Core Web Vitals
- Optimize Images and Videos: Reducing file sizes significantly improves page load speed. Compress images and videos and use appropriate file formats (e.g., WebP, AVIF).
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN stores website content on globally distributed servers, allowing users to retrieve data from the nearest server, thereby speeding up website loading.
- Code Optimization: Remove all unnecessary code, including extra spaces, comments, and unused code. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML to enhance loading speed.
- Enable Browser Caching: Caching allows browsers to store certain resources (e.g., images, CSS files) locally, speeding up page loading during subsequent visits.
- Reduce HTTP Requests: Minimize the number of elements on a page. Use CSS Sprites to combine multiple images into one, and reduce the number of scripts and style sheets to decrease HTTP requests and improve loading speed.
- Use High-Quality Servers and Reliable Hosting Services: These have a direct impact on website loading speed.
- Implement Lazy Loading: Lazy loading delays the download and loading of heavy resources (e.g., images) until they are needed, reducing the initial load time of the webpage.
7. Summary
Effective On-Page SEO strategies include:
- Accurate Keyword Targeting and Natural Integration: Seamlessly incorporating relevant keywords into content.
- High-Quality Content Creation: Producing valuable, engaging, and original content.
- Compelling Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Crafting titles and descriptions that attract clicks.
- Structured Use of H Tags: Organizing content with a clear hierarchy using H1 to H6 tags.
- Optimization of Images and Multimedia: Compressing images, using descriptive filenames, and adding alt text.
- Logical Internal Linking: Strategically placing internal links to enhance navigation and SEO.
- Significant Website Speed Improvements: Optimizing load times for better user experience and rankings.
On-Page SEO is a multi-dimensional, ongoing process that requires balancing technical details and user experience. It involves continuous adjustments to adapt to evolving search engine algorithms and changing user demands. Through these optimization measures, websites can achieve better visibility in search results, attract more visitors, and increase conversion rates.